Varicose veins (varicose veins) are among the most common circulatory disorders, which are accompanied by pathological changes in the vessels of the lower extremities, the formation of nodes and trophic ulcers. Patients also experience cramps and swelling that worsen with physical activity. Varicose veins on the legs are more common in women than in men. This is due to physiological properties.
The disease requires the help of specialists and well-organized control, since treating varicose veins on the legs without the help of specialists, especially if deep veins are affected, is risky. If treatment is ineffective, the risk of thrombophlebitis and other life-threatening complications increases sharply. Examining the signs of varicose veins in women and treating the disease is the responsibility of a phlebologist. You should contact this specialist if you notice vascular diseases of the lower extremities.
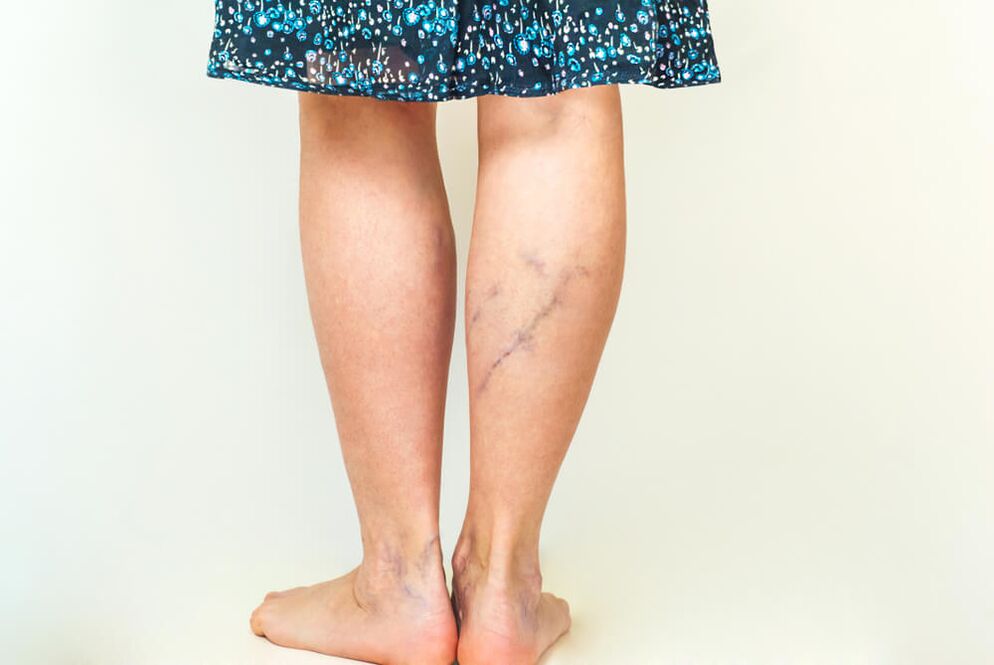
Signs of varicose veins
At the initial stage of the development of the disease, symptoms of varicose veins may be absent. A woman should pay attention to vascular changes in the legs, a tendency to evening swelling and discomfort in the legs. If all veins become more clearly visible, you should also pay attention to such changes.
Varicose veins of the legs in women are accompanied by the following symptoms:
- expanded capillary network, spider veins on legs;
- Feeling of heaviness and fatigue in the legs;
- swelling of the limbs;
- pain in the legs that worsens with prolonged standing or sitting;
- muscle cramps;
- trophic ulcers.
Sometimes varicose veins of internal organs develop in women, which are not always accompanied by external manifestations on the legs. In such cases, the pelvic area is most commonly affected. The disease occurs predominantly in women of active childbearing age.
Causes of varicose veins in women
The main cause of varicose veins on the legs in women is congestion of blood in the legs with subsequent disruption of the venous valve system. Causes can include hereditary weakness of the vein walls, increased strain on the limbs during pregnancy and wearing tight and uncomfortable shoes. A phlebologist can say exactly why varicose veins develop in the legs in a particular woman after studying the medical history and the results of a comprehensive examination.
Treatment of varicose veins in women
For swollen veins in women's legs, treatment can be conservative or surgical. Drug therapy is used at the initial stage of the development of the disease, when the pathology is not accompanied by serious dysfunction of the valve apparatus and the risk of complications.
The treatment regimen usually includes:
- Venotonics (phlebotonics);
- wearing compression stockings;
- the use of local ointments and creams that accelerate tissue healing, relieve heaviness and pain in the lower extremities, and reduce inflammation;
- Physical therapy.
Therapeutic treatment necessarily includes the use of phlebotonics in the form of capsules, ointments and gels.
Local remedies relieve swelling and heaviness in the legs and reduce swelling. If the swelling is severe, diuretics are prescribed. If there is still a risk of blood clots forming, antithrombotics are also indicated. Increased physical activity, work involving heavy lifting and long standing on the feet are contraindicated for the patient.
If these recommendations cannot be followed and the patient cannot change the type of activity, it is necessary to regularly perform exercises for the lower extremities to restore blood circulation and eliminate congestion. The shoes should be as comfortable as possible and should not pinch on the top or toes.
If you have varicose veins in the early stages, be sure to wear compression clothing - tights, stockings. They relieve pressure on the lower extremities and relieve pressure on the lymphatic system. Compression stockings do not make the nodes less noticeable and do not play a decisive role in the fight against the disease, but they help prevent the development of complications and slow down the progression of the pathology. If there is increased strain on the legs, we recommend wearing stockings. Compression garments must be worn after surgery to prevent blood clots.
Sclerotherapy
It is not always possible to cure varicose veins using only conservative methods. Therefore, phlebologists recommend not postponing surgery if your doctor insists. In most cases, the surgeon recommends surgery to remove the pathological nodes and restore normal blood circulation. If there are no contraindications, minimally invasive treatment methods are used, especially sclerotherapy. This involves the treatment of varicose veins with the help of special sclerosing drugs by introducing active substances into the lumen of the vessel, which lead to the collapse of the vessel walls and the termination of their participation in the blood circulation. The operation takes place without any skin incisions. The dilated vessels of the lower extremities gradually merge into connective tissue strands with the help of sclerosing substances and then dissolve and disappear.
Laser coagulation
If spider veins are present and small vessels are dilated, the surgeon may also recommend laser coagulation. Laser energy causes the coagulation of proteins. During laser coagulation, the doctor inserts a probe with a laser tip into the lumen of the damaged vein, as a result of which its walls are "sealed" and vascular spasms occur. The vessel is then replaced with connective tissue. The procedure is carried out under local anesthesia, there is no pain.
Over the course of several weeks, necrotic changes occur in the walls of the blood vessels, transforming the vein walls into strands of connective tissue. Blood no longer circulates through them because they fall out of circulation. However, coagulation of the venous walls of the lower extremities does not exclude relapse of the disease. Under the influence of unfavorable external and internal factors, intact vessels can expand with the formation of backflow and nodal deformation.
In the first few weeks after surgery, it is recommended to avoid physical exertion, spending long periods of time on your feet and wearing compression stockings or tights. Additionally, anticoagulant medications are prescribed to prevent blood clots from forming.
Phlebectomy
Phlebectomy is an operation in which the surgeon removes varicose veins, even deep ones. During the operation, the trunk of the great saphenous vein and pathologically changed tributaries are removed. At the same time, blood circulation is not disturbed, as they only make up 10% of the blood flow. The rest of the blood circulates in the deep vascular system.
Phlebectomy eliminates vertical reflux, horizontal outflow of blood and its pathological flow, which contributes to the progression of varicose veins even after minimally invasive surgical treatment methods. The operation is performed under general anesthesia.
Preventive measures
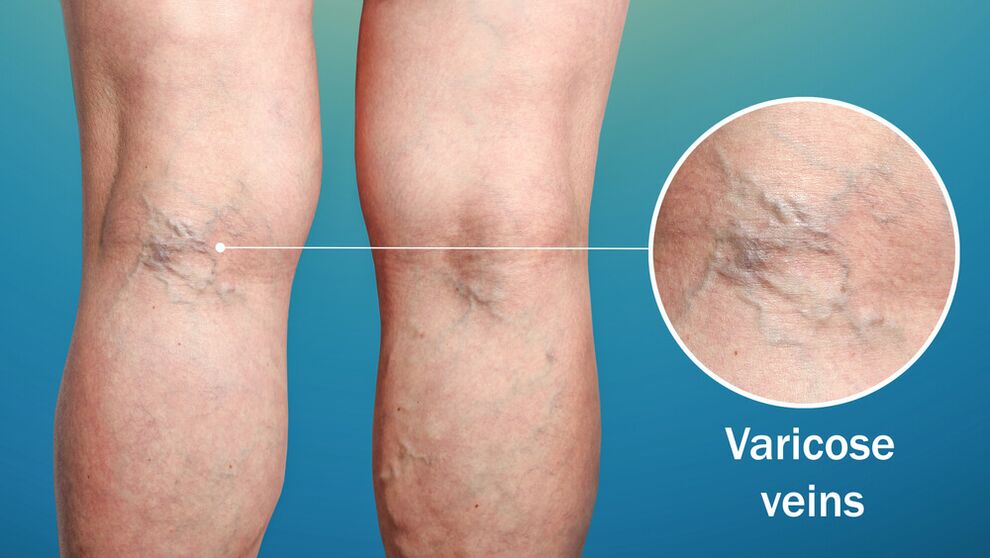
Varicose veins are a common circulatory disorder that can severely impact your quality of life. To prevent this disease, it is necessary to monitor the condition of the blood vessels in the legs and maintain a correct lifestyle.
It is recommended to avoid prolonged sitting and standing in one place. Prolonged static loads lead to overcrowding of the veins, expansion of their walls and deformation. Constant tension leads to blood congestion and increased pressure in the extremities. Regular breaks from work and exercises to relieve congestion in the legs help maintain the functionality of the valve system.
It is also very important to monitor your weight and eat right. Avoid fatty and salty foods as well as smoking and alcohol. These bad habits can make varicose veins more difficult to progress and increase the risk of complications. Wearing compression clothing is also an excellent addition to preventing venous disease. Elastic compression improves blood circulation and reduces strain on the limbs.
If you have to be on your feet for long periods of time or wear uncomfortable shoes, physical therapy is necessary. The aim is to restore normal blood flow in the legs and eliminate lymphatic congestion. It is recommended to carry out exercise therapy during breaks from work after severe fatigue. In addition, it is necessary to use venotonic agents in the form of cream, gel or ointment. Such drugs relieve discomfort, reduce swelling and prevent the development of varicose veins in the initial stages of the disease.